Diabetic Neuropathy
What is Diabetic Neuropathy?
Diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) is a common complication of diabetes, and its underlying cause is chronic hyperglycemia (high blood sugar levels). Over time, elevated glucose levels lead to several biochemical and structural changes that result in nerve damage, particularly to the peripheral nerves (nerves outside the brain and spinal cord).
Diabetic neuropathy is the most common type of peripheral neuropathy, affecting approximately 50% of individuals with diabetes, particularly those who have had the condition for several years or have poorly controlled blood sugar levels. This type of neuropathy occurs when high blood sugar levels cause damage to the peripheral nerves, most commonly in the feet, legs, and hands. The damage interferes with normal nerve function, leading to symptoms like numbness, tingling, pain, and weakness. As the leading cause of peripheral neuropathy, diabetic neuropathy is a significant concern for people with diabetes, underscoring the importance of early detection, proper blood sugar control, and timely intervention to manage symptoms and prevent further nerve damage.
What are the Most Common Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy Symptoms?
- Numbness or tingling in the feet, hands, or legs
- Burning pain or sharp, stabbing pain in the feet or hands
- Pins and needles sensation, especially in the extremities
- Loss of coordination and balance, leading to difficulty walking
- Increased sensitivity to touch, causing discomfort or pain from light touches (e.g., from bed sheets)
- Muscle weakness, especially in the lower legs or feet
- Pain that worsens at night, often making it hard to sleep
- Foot deformities, such as hammertoes or Charcot foot, due to muscle weakness
- Loss of reflexes, particularly in the feet and ankles
- Difficulty feeling temperature changes, which can lead to burns or frostbite
- Foot ulcers or wounds that are slow to heal
- Dry, cracked skin on the feet due to reduced sweating and poor circulation
- Foot drop, where the foot drags or cannot be lifted properly when walking
- Sharp, cramp-like sensations or muscle spasms in the feet or legs
- Loss of feeling in the extremities, increasing the risk of injury
These symptoms occur when the peripheral nerves in the arms, hands, feet, and legs are damaged due to high blood sugar levels. Early intervention and proper management are essential to reduce further nerve damage and improve quality of life.
What Causes Diabetic Neuropathy?
Diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) is a common complication of diabetes, and its underlying cause is chronic hyperglycemia (high blood sugar levels). Over time, elevated glucose levels lead to several biochemical and structural changes that result in nerve damage, particularly to the peripheral nerves (nerves outside the brain and spinal cord). The key mechanisms involved include:
Metabolic Stress and Oxidative Damage
(Polyol Pathway Activation)
In hyperglycemia, excess glucose is shunted into the polyol pathway, where the enzyme aldose reductase converts glucose into sorbitol. Accumulation of sorbitol within cells leads to osmotic stress, which damages the Schwann cells that form the myelin sheath of peripheral nerves. This disrupts nerve conduction.

Oxidative Stress
Elevated glucose levels increase the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), leading to oxidative damage of nerve cells. Mitochondria, the energy-producing structures in cells, are particularly vulnerable, which affects the energy supply needed for proper nerve function.
Vascular Insufficiency and Microvascular Damage
High blood sugar damages the small blood vessels (microangiopathy) that supply the nerves. These small vessels, or vasa nervorum, provide essential nutrients and oxygen to peripheral nerves. Damage to these vessels leads to ischemia (reduced blood supply), which causes nerve fiber degeneration.
Endothelial Dysfunction
Hyperglycemia impairs the function of endothelial cells, which line blood vessels and regulate vascular tone. This further reduces blood flow and the delivery of nutrients to nerves, contributing to nerve damage.
Chronic Inflammation and Immune Response
High glucose levels trigger a chronic inflammatory response. Pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukins, are upregulated and cause further damage to nerve fibers and supporting cells. Immune-mediated Damage: Some studies suggest that immune cells may also attack the peripheral nerves in diabetes, exacerbating the neuropathic process.
6. Advanced Glycation End Products (AGEs)
Chronic hyperglycemia results in the non-enzymatic glycation of proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids, forming advanced glycation end products (AGEs). AGEs accumulate in peripheral nerves, blood vessels, and Schwann cells, causing structural damage and disrupting the function of these tissues. AGEs also contribute to oxidative stress and inflammation.
7. Axonal Damage and Demyelination
Axonal Degeneration: The metabolic and vascular stress leads to axonal damage, particularly in long nerves, such as those that extend to the feet. This explains why diabetic peripheral neuropathy often starts in the lower extremities. Axonal degeneration impairs the transmission of signals between the nerves and muscles or sensory organs.
Demyelination: Schwann cells produce the myelin sheath, which insulates nerves and allows for the rapid transmission of nerve signals. Damage to Schwann cells leads to demyelination, resulting in slower nerve conduction and disrupted sensory or motor function.
Affected Structures by Diabetes
Peripheral Nerves: Sensory, motor, and autonomic nerves are affected, but sensory nerves are often more vulnerable, leading to symptoms such as numbness, tingling, and pain.
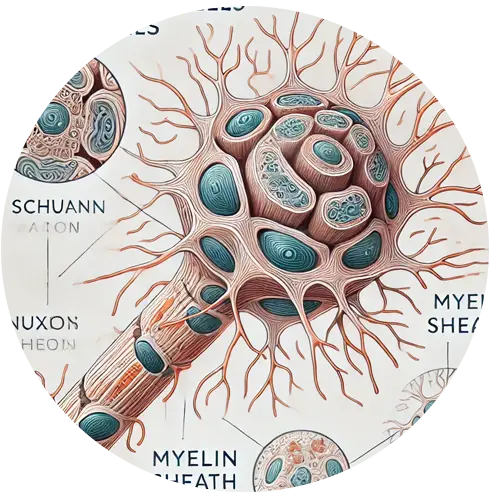
Schwann Cells: Supporting cells that form the myelin sheath around nerves, which are crucial for proper nerve function.
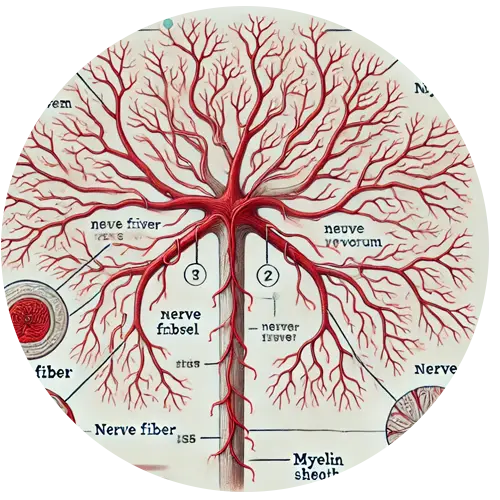
Vasa Nervorum: Small blood vessels that supply peripheral nerves, which become damaged, leading to nerve ischemia.

Nerve Axons: The long projections of neurons that transmit signals to other neurons, muscles, or glands.
What are the Different Types of Diabetic Neuropathy?
There are several types of diabetic neuropathy, each affecting different parts of the nervous system. The main types of diabetic neuropathy are:

Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy is the most common form of diabetic neuropathy. It affects the sensory nerves in the extremities, particularly the feet and legs, but can also impact the hands and arms. This condition typically begins with numbness or tingling sensations in the toes and gradually spreads up the legs or arms. It is often associated with pain, weakness, and loss of coordination.
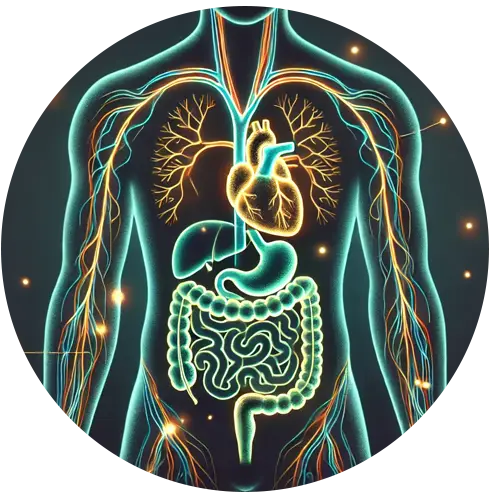
Autonomic Neuropathy
Autonomic neuropathy involves the nerves that control involuntary bodily functions such as heart rate, blood pressure, digestion, and sweating. Damage to these nerves can result in a range of symptoms, including issues with heart rate, digestive problems, and problems with bladder control. It can also lead to blood pressure irregularities and difficulty regulating body temperature.

Proximal Neuropathy
Proximal neuropathy, also known as diabetic amyotrophy, typically affects the hips, thighs, and buttocks. It often causes severe pain and muscle weakness, particularly in the legs. The condition is more common in older adults with diabetes and can impact one side of the body before affecting both sides.

Focal Neuropathy
Focal neuropathy affects a single nerve or a specific group of nerves, typically in the head, torso, or legs. It can cause sudden pain, weakness, or paralysis in the affected area. Common forms of focal neuropathy include pain around the eyes, difficulty moving a particular muscle, or chest pain that mimics a heart attack.
How is Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy Diagnosed at Neuropathy Relief Center Of Miami?
At the Neuropathy Relief Center of Miami a neuropathy consultation will be performed to understand your individual symptoms, complaints, and medical history. After your consultation, Dr. Alfonso will perform a neuropathy examination and if necessary order additional advanced testing to help diagnose your individual neuropathy condition.
During your specialized neuropathy physical and neurologic exam, Dr. Alfonso will check your motor and sensory functions. He will utilize multiple tests for muscle strength, size and tone, reflexes, balance and coordination, and study your ability to feel sensations (vibrations, hot, cold, sharp, dull, light touch). Orthopedic testing and any needed x-rays will also be performed to determine if you have a compressive or entrapment type of neuropathy in combination of diabetic peripheral neuropathy.
After the completion of the neuropathy consultation and examination Dr. Alfonso and his healthcare team will thoroughly study your results, determine if you are a good candidate for specialized neuropathy treatment and develop your treatment plan and recommendations.
What is the Best Diabetic Neuropathy Treatment and Why?
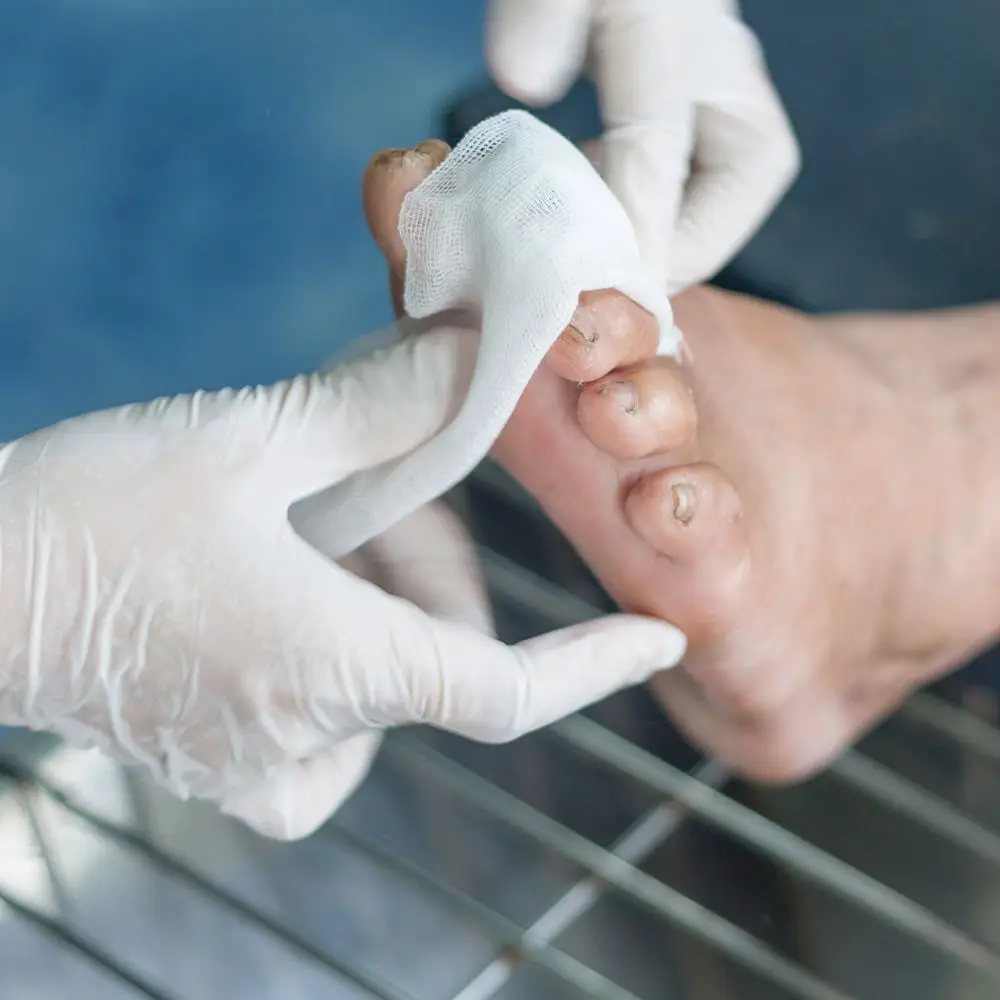

The underlying cause of diabetic peripheral neuropathy is prolonged hyperglycemia, which results in metabolic, vascular, and inflammatory damage to peripheral nerves. Specific damage occurs to the axons, Schwann cells, and the small blood vessels supplying the nerves, leading to impaired nerve conduction, nerve degeneration, and the characteristic symptoms of neuropathy.
Currently, Conventional medicine does not have a cure for people who suffer from peripheral neuropathy.
Patients are prescribed powerful medications (painkillers, antidepressants, antiseizure) that do not treat the cause of the damaged peripheral nerves causing the pain, numbness, discoloration, cramping, restless legs, and balance issues.
Unfortunately these medications do not rehabilitate the damaged blood vessels or damaged peripheral nerves that are causing the neuropathy symptoms (Nerve Cell Death) and results worsening of their condition.
Dr. Alfonso‘s Neuropathy Treatment Protocol is a highly successful drug-free, non surgical, safe, and effective treatment that has successfully helped many patients who suffer from Diabetic Neuropathy
Unlike traditional treatments that primarily focus on masking the symptoms with of diabetic neuropathy, Dr. Alfonso’s Neuropathy Treatment Protocol aims to address the underlying causes of peripheral neuropathy. This comprehensive approach combines specialized therapies to rehabilitate damaged nerves and restore nerve function. The treatment plan, tailored to each patient’s needs through consultation, examination, and diagnostics, includes:

Improved circulation: Enhancing blood flow to damaged peripheral nerves increases the delivery of oxygen and nutrients essential for blood vessel and nerve healing.
Nerve regeneration: Stimulating the growth of new nerve cells helps repair the damaged peripheral nerves, promoting long-term recovery.

Eliminating nerve compression: Removing mechanical entrapment or compression in the spine and extremities allows the nerves to function properly again. By targeting the root causes of diabetic neuropathy, this protocol helps restore nerve health rather than merely alleviating pain.
How successful is the Dr. Alfonso Neuropathy Treatment Protocol for Diabetic Neuropathy?
We see an estimated successful 85% improvement rate in our patients. Every patient’s case is unique with their own specific complicating factors and results vary depending on compliance to care, chronicity and other health conditions. Our patients report diabetic neuropathy symptom and functional loss improvements such as burning, sharp stabbing pain, pins and needles, numbness and tingling, improved balance and walking abilities, more restful sleep and the ability to enjoy normal life activities with friends and family.
How to Prevent Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy

Control your blood sugar levels. This is the most important thing you can do to prevent DPN.

Get regular exercise. Exercise helps to keep your blood sugar levels in check and can also help to improve circulation.

Eat a healthy diet. A healthy diet can help to keep your blood sugar levels in check and can also provide your body with the nutrients it needs to heal.
Take care of your feet. Keep your feet clean and dry, and inspect them regularly for any signs of problems.

Don’t smoke. Smoking damages the nerves and can increase your risk of developing DPN.
Call Us For a Complimentary
Consultation
(305) 275-7475
Request a free consultation with Dr. Alfonso to learn how you can naturally treat your symptoms of Neuropathy without any invasive procedures, surgery, or harmful medications.
Follow us on Instagram, Facebook, and YouTube for updates, patient success stories, and expert insights on neuropathy treatment!